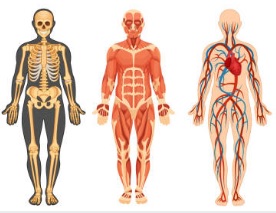
Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body. It consists the examination and understanding of the various systems, organs, tissues, and cells that constitute the human organism. Here is a brief overview of the major components and systems of human anatomy:
Skeletal System:
- Bones: The human skeleton gives structural support, protects main organs, and facilitates movement. There are 206 bones in the adult human body.
- Joints: Points where bones articulate and allow for movement.
Muscular System:
- Muscles: Tissues responsible for movement by contracting and relaxing. Muscles are attached to bones by tendons.
- Types of Muscles: Skeletal muscles , smooth muscles (involuntary, found in organs), and cardiac muscles (involuntary, found in the heart).
Nervous System:
- Brain: The control center of the body, responsible for processing information and controlling body functions.
- Spinal Cord: A bundle of nerves that facilitates communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
- Nerves: Transmit signals throughout the body.
Circulatory System:
- Heart: Pump that circulates blood throughout the body.
- Blood Vessels: Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
- Blood: Carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Respiratory System:
- Lungs: Organs responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood.
- Trachea and Bronchi: Conduct air to and from the lungs.
- Diaphragm: Muscle that aids in breathing.
Digestive System:
- Mouth, Esophagus, and Stomach: Organs involved in the breakdown of food.
- Small and Large Intestines: Absorb nutrients and water from digested food.
- Liver and Pancreas: Produce digestive enzymes and regulate metabolism.
Urinary System:
- Kidneys: Filter blood, remove waste products, and produce urine.
- Bladder: Stores urine before excretion.
Reproductive System:
- Male Reproductive System: Includes testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and penis.
- Female Reproductive System: Includes ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina.
Endocrine System:
- Glands: Produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
- Hormones: Chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to target organs.
Integumentary System:
- Skin: Largest organ, provides protection, regulates temperature, and houses sensory receptors.
Lymphatic System:
- Lymph Nodes: Filter lymph (a fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system) and help fight infection.
- Spleen and Thymus: Organs that play roles in immune function.